Understanding Search Engines: A Beginner’s Guide
Introduction
Welcome to our beginner’s guide on search engines! Search engines play a vital role in our daily lives, helping us find information, services, and products online. If you’ve ever wondered how search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo work, or why some websites appear higher in the results than others, you’re in the right place. In this guide, we’ll explore the inner workings of search engines, delve into Google’s local ranking algorithm, and understand the various components of search engine results pages (SERPs).
How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines follow three primary steps to provide relevant search results: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
Crawling
Search engines send out bots, also known as spiders or crawlers, to explore the internet. These bots systematically browse the web, following links from one page to another and collecting data about each webpage they visit. Crawling is a continuous process, ensuring that search engines have the most up-to-date information about the web. The crawlers look for new content, updates to existing content, and dead links, gathering data to be analyzed and indexed.
Indexing
The information collected by the crawlers is then stored in a massive database known as the index. This index is like a giant library where the search engine organizes and categorizes the web pages. Each page is analyzed and stored based on its content, keywords, and other factors. When a page is indexed, it means that the search engine has processed and included it in its database, making it available for retrieval during a search. However, not all pages are indexed—only those that meet certain criteria and quality standards.
Ranking
When you search for something, the search engine looks through its index and ranks the pages based on relevance and quality. This ranking process determines the order in which the results appear on the search engine results pages (SERPs). Factors that influence ranking include the content’s relevance to the search query, the quality and authority of the website, and the user’s location and search history. Google’s ranking algorithm is complex and considers over 200 factors, including keywords, site speed, mobile-friendliness, and backlinks.

Why Might a Page Not Be Indexed?
There are several reasons why a page might not be indexed by search engines. Understanding these reasons can help you diagnose and fix issues to ensure your content is discoverable.
Noindex Tag
If a page has a “noindex” meta tag, it tells search engines not to include it in their index. This tag is useful for pages you don’t want to appear in search results, but if applied unintentionally, it can prevent important content from being indexed.
Crawl Errors
If search engine bots encounter errors while trying to crawl your page, such as server errors (5xx), they may not be able to index the page. Regularly checking Google Search Console for crawl errors can help you identify and fix these issues.
Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file can be used to block search engines from crawling certain pages or sections of your website. If a page is disallowed in the robots.txt file, it won’t be indexed. Ensure your robots.txt file is correctly configured to allow search engines to crawl important pages.
Duplicate Content
Search engines avoid indexing multiple pages with identical or very similar content. If your page has duplicate content, it may not be indexed, or the search engine might choose to index only one version. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page.
Lack of Internal Links
Pages that are not linked from other parts of your website may be difficult for search engines to discover. Ensure all important pages are included in your site’s internal linking structure.
Low-Quality Content
Search engines aim to provide users with high-quality, relevant content. Pages with thin, duplicate, or low-quality content may not be indexed. Focus on creating valuable, unique content that meets user needs.
New or Recently Updated Page
It can take some time for search engines to discover and index new or recently updated pages. Patience is key, but you can also speed up the process by submitting your sitemap to search engines and using tools like Google Search Console to request indexing.
Penalties
If your website has been penalized for violating search engine guidelines, certain pages or even the entire site may be excluded from the index. Address any violations and request reconsideration if your site has been penalized.
By addressing these issues, you can improve the chances of your pages being indexed and appearing in search results, thereby increasing your website’s visibility and traffic.
Introduction to Google’s Algorithm for Local Ranking
Local SEO is all about optimizing your online presence to attract more business from relevant local searches. For example, if you own a coffee shop in New York, you want to appear in searches like “coffee shop near me” or “best coffee in New York.” Google’s algorithm for local ranking focuses on several key factors to determine which businesses are most relevant to local searchers.
Relevance
Relevance refers to how well a local business listing matches what someone is searching for. Adding complete and detailed business information can help Google better understand your business and match your listing to relevant searches. This includes your business name, address, phone number, and a detailed description of your services.
Distance
Distance considers how far each potential search result is from the location term used in a search. If a user doesn’t specify a location in their search, Google will calculate distance based on what it knows about their location. This means that businesses closer to the user or the specified location are more likely to rank higher in local search results.
Prominence
Prominence refers to how well-known a business is. Some places are more prominent in the offline world, and search results try to reflect this in local ranking. For example, famous museums, landmark hotels, or well-known store brands that are familiar to many people are also likely to be prominent in local search results. Prominence is also based on information that Google has about a business from across the web, such as links, articles, and directories. Google My Business is a critical tool for local SEO. By verifying and updating your business information, you can help customers find you and tell them the story of your business. Positive reviews and interactions on your Google My Business profile can also boost your prominence.
Overview of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs)
When you enter a query into a search engine, the page you see with all the results is called the Search Engine Results Page (SERP). SERPs have evolved significantly over the years and now include a variety of different types of results designed to provide the most relevant information to users.
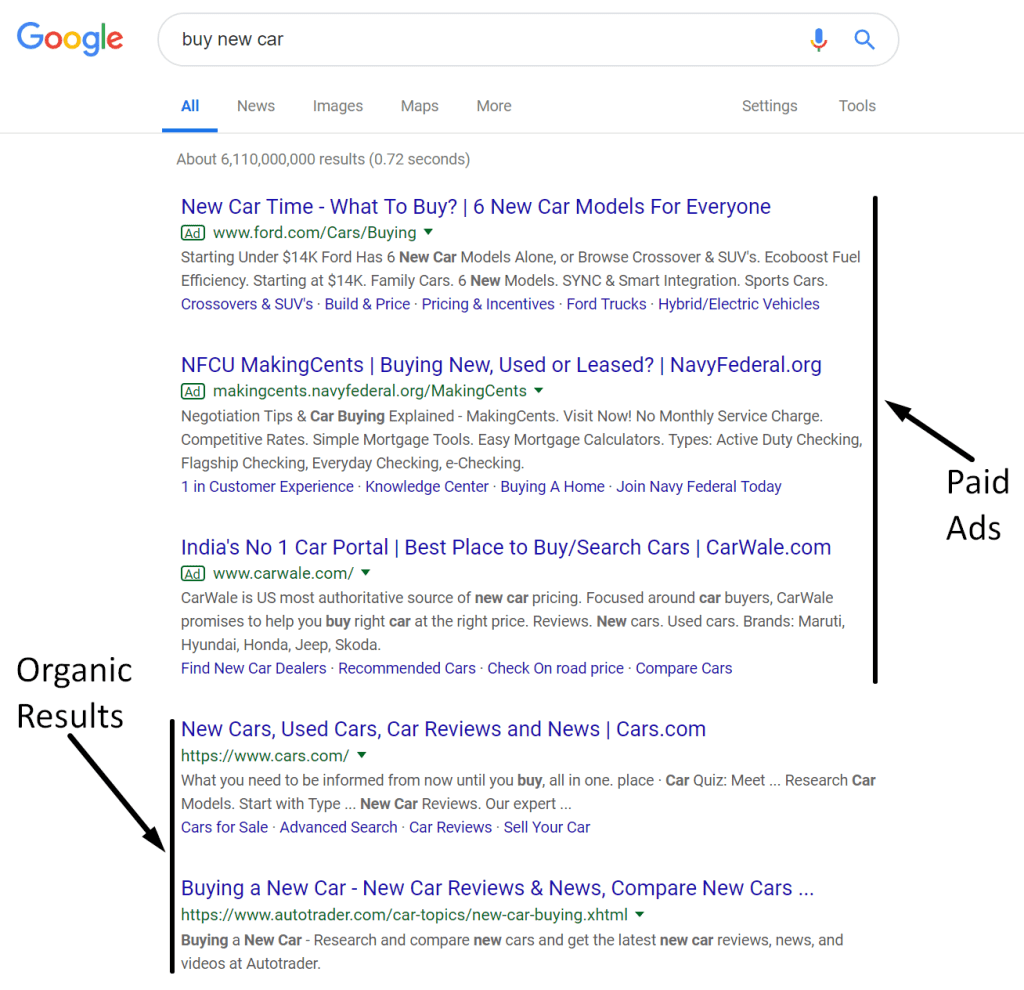
Organic Results
These are the natural search results ranked based on their relevance to the search query and quality of content. SEO primarily focuses on improving these results. Organic results are not influenced by advertising payments, making them a critical area for businesses to focus on for long-term visibility.
Paid Results
These are advertisements that appear at the top or bottom of the SERP. Businesses pay to have their websites displayed when specific keywords are searched. These ads are typically marked with a small “Ad” label. Paid search, also known as pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, can be a quick way to gain visibility, especially for competitive keywords.
Featured Snippets
These are selected search results that are displayed on top of Google’s organic results, in a box. They aim to answer the user’s query directly on the SERP. Featured snippets can be in the form of a paragraph, list, table, or video. Getting your content featured in a snippet can significantly increase your visibility and click-through rates.
Local Pack
This is a set of three local business listings that appear for searches with local intent. It includes a map showing the locations of the businesses, along with their names, ratings, and other relevant information. The local pack is a crucial feature for businesses that rely on local customers, as it provides high visibility right at the top of the SERP.
Search Engine Algorithms
Different search engines use various algorithms to rank websites. While Google is the most widely used search engine, understanding how other search engines like Bing and Yahoo work can also be beneficial.
Google: Google uses a complex algorithm with over 200 ranking factors, including relevance, quality, and user experience. Google’s algorithm is continuously updated to improve the accuracy and relevance of search results. Major updates, such as Panda, Penguin, and Hummingbird, have significantly impacted how websites are ranked.
Bing: Bing, owned by Microsoft, also uses a unique algorithm to rank search results. While similar to Google’s, Bing places more emphasis on social signals, such as how often a website or page is shared on social media platforms. Bing also integrates with Windows and other Microsoft products, affecting search results.
Yahoo: Yahoo Search is powered by Bing, so the ranking algorithms are quite similar. However, Yahoo has its own features and integrations, particularly with other Yahoo services and content.
Algorithm Updates: Search engine algorithms are regularly updated to enhance user experience and combat spammy or manipulative practices. Staying informed about these updates is crucial for maintaining and improving your website’s ranking.
The Future of Search Engines
As technology evolves, so do search engines. Here are some trends shaping the future of search:
Voice Search
With the rise of smart speakers and voice assistants like Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri, voice search is becoming increasingly popular. Voice search queries are often longer and more conversational, requiring different SEO strategies.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are playing a more significant role in search engine algorithms. These technologies help search engines understand user intent better and provide more personalized and relevant results.
Mobile Search Trends
With the growing use of smartphones, mobile search has surpassed desktop search. Search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites, and Google’s mobile-first indexing means that the mobile version of your site is considered the primary version.

Conclusion
Understanding how search engines work is essential for anyone looking to improve their online presence. By grasping the basics of crawling, indexing, and ranking, you can better appreciate the complexity and importance of SEO. Local SEO is particularly crucial for businesses looking to attract nearby customers, and tools like Google My Business can significantly enhance your visibility. Keeping up with changes in search engine algorithms and embracing future trends like voice search and AI will help you stay ahead in the digital landscape. Stay curious, keep learning, and you’ll be well on your way to mastering search engines!



